Embark on a journey of psychological exploration with our AP Psych Midterm Study Guide, a comprehensive companion meticulously crafted to illuminate the intricacies of the human mind. Immerse yourself in a tapestry of knowledge, unraveling the fundamental concepts, biological foundations, and captivating phenomena that shape our thoughts, behaviors, and interactions.
Delve into the depths of sensation and perception, unraveling the mysteries of how we process and interpret the world around us. Explore the complexities of learning, uncovering the mechanisms that shape our knowledge and skills. Delve into the realm of cognition, deciphering the processes that govern our thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Key Concepts
Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It seeks to understand how people think, feel, and act, and how these processes are influenced by their environment and experiences.
The midterm will cover a range of fundamental concepts in psychology, including:
Methods of Research
Psychologists use a variety of research methods to study behavior and mental processes. These methods include:
- Observational research: Observing and recording behavior in a natural setting.
- Experimental research: Manipulating one or more variables to determine their effects on behavior.
- Correlational research: Examining the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them.
Experimental Designs
Psychologists use a variety of experimental designs to control for confounding variables and ensure that their results are valid. These designs include:
- Between-subjects design: Each participant is randomly assigned to one of two or more groups.
- Within-subjects design: Each participant experiences all of the experimental conditions.
- Matched-pairs design: Participants are matched on one or more characteristics before being assigned to different experimental conditions.
Terms and Definitions
The following is a list of key terms and definitions that you should be familiar with for the midterm:
- Behavior: Any observable action or response.
- Cognition: The mental processes involved in acquiring knowledge and understanding.
- Emotion: A complex psychological state that involves feelings, thoughts, and physiological changes.
- Personality: The unique combination of traits and characteristics that make each person different.
- Social psychology: The study of how people think, feel, and behave in social situations.
Biological Bases of Behavior
The biological bases of behavior delve into the intricate relationship between the physical structures and functions of the human body and our psychological experiences and behaviors. This field of study explores how our nervous system, hormones, and genetics contribute to shaping our thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Structure and Function of the Nervous System
The nervous system, composed of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, acts as the control center of the body, receiving, processing, and transmitting information. The brain, the most complex organ in the body, is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as memory, learning, and decision-making.
The spinal cord serves as the main communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, while peripheral nerves transmit sensory and motor information to and from the brain.
Neurotransmitters and Hormones
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons, the building blocks of the nervous system. Hormones, on the other hand, are chemical messengers that are released by glands into the bloodstream and travel throughout the body, influencing various physiological and behavioral processes.
- Neurotransmitters:Dopamine (reward and motivation), serotonin (mood and sleep), norepinephrine (arousal and attention), GABA (inhibition)
- Hormones:Testosterone (aggression and dominance), estrogen (reproduction and mood), cortisol (stress response), oxytocin (social bonding)
Role of Genetics in Psychology
Genetics play a significant role in shaping our behavior, influencing traits such as personality, intelligence, and susceptibility to mental disorders. Genes, which are units of heredity, carry the instructions for the development and functioning of an organism.
- Twin studies:Compare identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins to estimate the heritability of traits.
- Genome-wide association studies (GWAS):Identify specific genetic variants associated with particular traits or disorders.
- Epigenetics:Study of how environmental factors can influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence.
Sensation and Perception
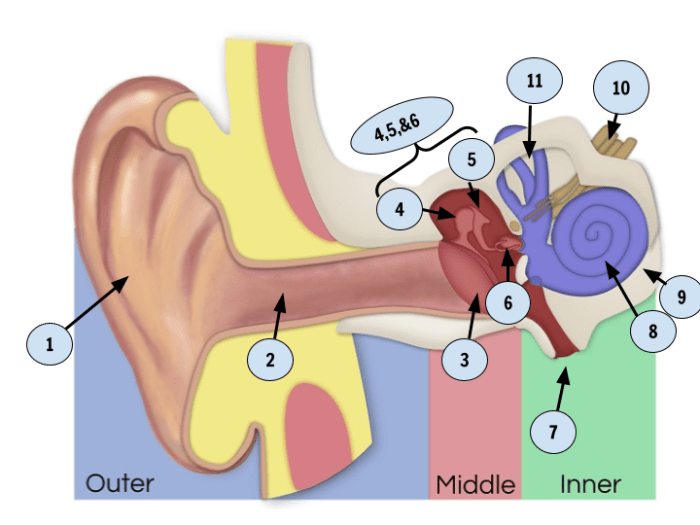
Sensation and perception are the processes by which we receive and interpret sensory information from the world around us. Sensation is the process of detecting physical stimuli, while perception is the process of organizing and interpreting those stimuli into meaningful experiences.
Sensory Systems
Our sensory systems are specialized to detect specific types of stimuli. The five main sensory systems are:
- Vision: Detects light waves
- Hearing: Detects sound waves
- Smell: Detects chemical molecules in the air
- Taste: Detects chemical molecules in food
- Touch: Detects pressure, temperature, and pain
Each sensory system has specialized receptors that convert physical stimuli into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to the brain, where they are processed and interpreted.
Principles of Perception
Perception is not a passive process. Our brains actively organize and interpret sensory information based on our past experiences and expectations. This process is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Attention: We can only focus on a limited amount of information at a time.
- Illusions: Our brains can sometimes be fooled by sensory information, leading to perceptual errors.
- Perceptual organization: Our brains tend to organize sensory information into meaningful patterns.
Role of Attention
Attention is the process of focusing on specific stimuli while ignoring others. Attention is essential for selective processing, which allows us to focus on the most important information in our environment.There are two main types of attention:
- Top-down attention: Controlled by our goals and expectations.
- Bottom-up attention: Captures our attention based on the salience of the stimuli.
Attention is a complex process that is influenced by a number of factors, including our motivation, emotions, and cognitive abilities.
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new knowledge, skills, or behaviors. It involves a change in behavior as a result of experience. There are three main types of learning: classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning.
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is a type of learning in which a neutral stimulus is paired with a meaningful stimulus, causing the neutral stimulus to eventually elicit the same response as the meaningful stimulus. For example, if a dog is repeatedly given a treat after hearing a bell, the dog will eventually salivate at the sound of the bell, even in the absence of the treat.
Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which the consequences of a behavior determine whether the behavior is repeated. Positive reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, while negative reinforcement decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
For example, if a child is given a sticker for cleaning their room, they are more likely to clean their room in the future.
Observational Learning
Observational learning is a type of learning in which an individual learns by observing the behavior of others. This type of learning is also known as social learning or modeling. For example, if a child sees their parents recycling, they are more likely to recycle themselves.
Factors that Influence Learning
There are a number of factors that can influence learning, including:
- Reinforcement and punishment: Reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, while punishment decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Motivation: Motivation is the desire to achieve a goal. People who are motivated are more likely to learn new things.
- Attention: Attention is the ability to focus on a particular stimulus. People who are paying attention are more likely to learn new things.
- Memory: Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information. People who have a good memory are more likely to learn new things.
Cognition
Cognition encompasses the mental processes involved in acquiring knowledge and understanding, including thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, and language comprehension. It enables us to perceive, interpret, and respond to the world around us.
Thinking
Thinking refers to the cognitive process of manipulating information in our minds. It involves activities like reasoning, concept formation, and judgment. Thinking allows us to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information to form conclusions and make decisions.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a cognitive process that involves finding solutions to challenges or obstacles. It requires identifying the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating them, and selecting the most appropriate one. Problem-solving skills are essential for adapting to new situations and overcoming difficulties.
Decision-Making
Decision-making is the cognitive process of choosing among multiple options. It involves weighing the pros and cons of each option, considering potential outcomes, and selecting the best course of action. Decision-making skills are crucial for making informed choices in various aspects of life.
If you’re grinding through that AP Psych midterm study guide, don’t forget to check out the AC Theory Level 1 Lesson 1 for some extra insights. It’s a great way to supplement your studies and boost your confidence heading into the exam.
Language
Language plays a vital role in cognition. It allows us to communicate our thoughts and ideas, express ourselves, and interact with others. Language shapes our perception of the world and influences our cognitive development. It enables us to categorize, organize, and retrieve information, facilitating higher-order thinking processes.
Development of Cognitive Abilities
Cognitive abilities undergo significant development throughout the lifespan. Infants and toddlers acquire basic cognitive skills such as object permanence and simple problem-solving. As children grow, their cognitive abilities expand, allowing for more complex thinking, reasoning, and memory. Adolescents develop abstract reasoning and critical thinking skills.
In adulthood, cognitive abilities may reach their peak, although they can continue to change and adapt with experience and learning.
Motivation and Emotion
Motivation and emotion are two closely related psychological concepts that play a crucial role in shaping our behavior. Motivation refers to the internal processes that drive us to engage in specific actions, while emotions are the subjective experiences that accompany these actions.
Understanding the relationship between motivation and emotion is essential for comprehending human behavior.
Theories of Motivation
There are several theories that attempt to explain the different types of motivation. One prominent theory is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which proposes that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom and self-actualization needs at the top.
Other theories include drive theory, which suggests that motivation is driven by internal physiological needs, and incentive theory, which emphasizes the role of external rewards in motivating behavior.
The Role of Emotions in Behavior
Emotions are powerful psychological forces that can influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions. They can motivate us to approach or avoid certain situations, and they can affect our decision-making processes. For example, fear can motivate us to avoid dangerous situations, while joy can motivate us to seek out pleasurable experiences.
The Relationship between Motivation and Emotion, Ap psych midterm study guide
Motivation and emotion are closely intertwined. Emotions can influence our motivation, and motivation can influence our emotions. For example, if we are highly motivated to achieve a goal, we may experience positive emotions such as excitement and anticipation. Conversely, if we are not motivated to complete a task, we may experience negative emotions such as boredom and frustration.
Development: Ap Psych Midterm Study Guide

Development is a lifelong process that involves changes in physical, cognitive, and social-emotional aspects. It is influenced by both genetics and the environment.
The major stages of human development include:
- Infancy (birth to 1 year)
- Toddlerhood (1 to 3 years)
- Preschool (3 to 5 years)
- School age (6 to 12 years)
- Adolescence (13 to 18 years)
- Young adulthood (19 to 40 years)
- Middle adulthood (40 to 65 years)
- Late adulthood (65 years and older)
Factors Influencing Development
Genetics and environment play significant roles in shaping development. Genetics provide the blueprint for physical and cognitive development, while the environment provides the experiences that shape social-emotional development.
Attachment
Attachment is a strong emotional bond between a child and their caregiver. It plays a crucial role in development by providing a sense of security and stability, which is essential for healthy physical, cognitive, and social-emotional development.
Personality
Personality refers to the enduring patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that characterize an individual. It encompasses the unique ways in which people think about themselves, others, and the world around them, and how they respond to different situations.
There are numerous theories that attempt to explain the development and structure of personality. Some of the most prominent include:
- Psychoanalytic theory: This theory, developed by Sigmund Freud, emphasizes the role of unconscious processes, childhood experiences, and defense mechanisms in shaping personality.
- Behavioral theory: This theory, associated with B.F. Skinner, focuses on the role of learning and reinforcement in shaping behavior and personality.
- Humanistic theory: This theory, developed by Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow, emphasizes the importance of self-actualization, free will, and personal growth in personality development.
- Trait theory: This theory, developed by Gordon Allport and Raymond Cattell, proposes that personality can be described in terms of a set of stable traits that are relatively consistent over time and across situations.
- Social cognitive theory: This theory, developed by Albert Bandura, emphasizes the role of social learning, self-efficacy, and cognitive processes in shaping personality.
The assessment and measurement of personality is a complex and challenging task. There are a variety of methods used to assess personality, including:
- Interviews: Interviews involve asking individuals questions about their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Questionnaires: Questionnaires consist of a series of questions that individuals answer on a self-report basis.
- Projective tests: Projective tests present individuals with ambiguous stimuli and ask them to interpret them, which can reveal unconscious thoughts and feelings.
- Observational methods: Observational methods involve observing individuals in different situations to assess their behavior.
The role of culture in personality development is significant. Culture provides individuals with a set of values, beliefs, and norms that shape their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Cultural factors can influence personality development in a variety of ways, including:
- Socialization: Culture is transmitted to individuals through socialization processes, which teach them the values, beliefs, and norms of their society.
- Language: Language is a key aspect of culture that can influence personality development by providing individuals with a set of concepts and ways of thinking.
- Social roles: Culture defines a set of social roles that individuals are expected to play, which can influence their self-concept and behavior.
Abnormal Psychology

Abnormal psychology examines mental disorders, their causes, treatments, and the stigma associated with them.Mental disorders are characterized by significant disturbances in thinking, emotion, or behavior that impair daily functioning. They can range from mild to severe and include conditions such as anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
Causes of Mental Disorders
The causes of mental disorders are complex and involve a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. Biological factors include genetic predispositions, neurochemical imbalances, and brain abnormalities. Psychological factors include early life experiences, trauma, and stress. Social factors encompass environmental influences, social support, and cultural norms.
Treatments for Mental Disorders
Treatment for mental disorders typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or psychodynamic therapy, helps individuals identify and change maladaptive thoughts and behaviors. Medication, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics, can alleviate symptoms and improve functioning.
Self-help strategies, such as exercise, healthy sleep habits, and social support, can complement professional treatment.
Stigma in Mental Health
Stigma surrounding mental illness remains a significant barrier to seeking help. Fear of judgment, discrimination, and social isolation can prevent individuals from acknowledging or seeking treatment for their condition. Combating stigma involves educating the public about mental disorders, promoting awareness, and encouraging empathy and understanding.
Social Psychology
Social psychology delves into the intricate interplay between individuals and their social environment. It encompasses a broad spectrum of subfields, including social cognition, social influence, and group dynamics.
Social Cognition
Social cognition explores how individuals process, store, and apply information about others. This includes forming impressions, making judgments, and understanding social interactions.
Social Influence
Social influence examines the ways in which individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are shaped by others. This can occur through conformity, persuasion, or obedience.
Group Dynamics
Group dynamics focuses on the behavior of individuals within groups. It examines how group size, composition, and norms affect group processes and outcomes.
Culture and Social Behavior
Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping social behavior. Cultural values, beliefs, and norms influence how individuals perceive and interact with others.
Prejudice and Discrimination
Prejudice and discrimination are significant social problems that involve negative attitudes and behaviors towards certain groups of people. They can have devastating consequences for individuals and society as a whole.
Questions and Answers
What topics are covered in the AP Psych Midterm Study Guide?
The study guide covers all the key concepts tested on the AP Psych midterm, including biological bases of behavior, sensation and perception, learning, cognition, motivation and emotion, development, personality, abnormal psychology, and social psychology.
How can I use the study guide effectively?
Use the study guide as a supplement to your class notes and textbook. Review the material regularly, take practice tests, and seek clarification on any concepts you don’t understand.
What resources are available to help me with my AP Psych midterm?
In addition to the study guide, there are many online resources available, such as practice tests, flashcards, and videos. You can also join study groups or seek help from your teacher or a tutor.
