Embark on a comprehensive exploration of Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test, a groundbreaking tool that revolutionizes the accuracy and efficiency of medication administration. This detailed guide delves into the intricacies of weight-based dosing, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
By understanding the fundamental principles, potential pitfalls, and practical applications of dosage calculation, healthcare providers can confidently navigate the complexities of medication administration, ensuring that every patient receives the precise dosage they need for optimal therapeutic effects.
1. Dosage Calculation Methods: Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage By Weight Test
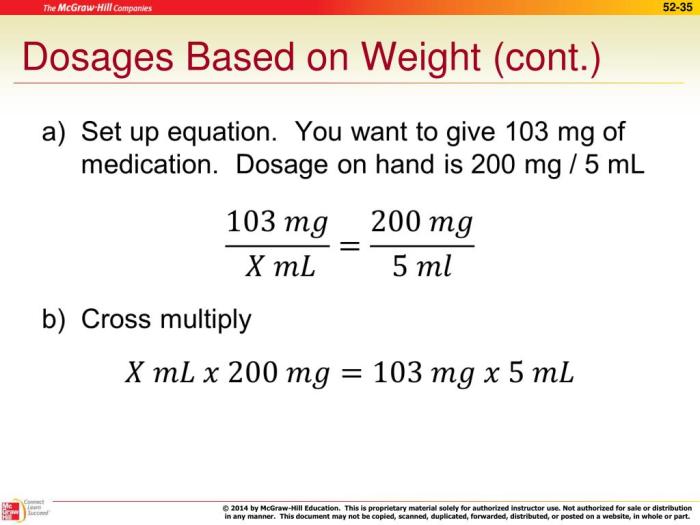
Dosage calculation based on weight involves determining the appropriate amount of medication to administer based on the patient’s weight. It is a crucial aspect of healthcare as it ensures that patients receive the correct dosage for their specific needs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Dosage Calculation by Weight
- Determine the patient’s weight in kilograms.
- Multiply the patient’s weight by the recommended dosage per kilogram.
- The result is the total dosage to be administered.
Methods for Dosage Calculation by Weight
- Milligrams per Kilogram (mg/kg):The most common method, where the dosage is expressed in milligrams per kilogram of body weight.
- Micrograms per Kilogram (mcg/kg):Used for medications with very small doses.
- Units per Kilogram (U/kg):For medications measured in units, such as insulin.
2. Factors Influencing Dosage Calculation

Several factors can influence dosage calculation by weight, affecting the amount of medication required.
Age
The age of the patient can impact dosage calculations, as younger patients may require lower doses than adults.
Weight
Weight is the primary factor considered in dosage calculation, as it directly determines the amount of medication needed.
Medical Condition
The patient’s medical condition can also influence dosage calculations. For example, patients with liver or kidney disease may require adjusted dosages.
Adjusting Dosage Calculations
Healthcare professionals may need to adjust dosage calculations based on these factors. This involves considering the patient’s age, weight, and medical condition, and using appropriate formulas or guidelines.
3. Common Errors in Dosage Calculation
Errors in dosage calculation can have serious consequences for patients. Common errors include:
- Using the wrong weight:Using an incorrect weight can lead to overdosing or underdosing.
- Misreading the dosage instructions:Misinterpreting the dosage instructions can result in incorrect dosage calculations.
- Incorrect conversion between units:Failing to correctly convert between different units of measurement can lead to errors.
Consequences of Errors
Dosage calculation errors can result in:
- Medication toxicity
- Therapeutic failure
- Patient harm
Preventing Errors
To prevent errors, healthcare professionals should:
- Use accurate and up-to-date patient information.
- Double-check dosage calculations.
- Use electronic dosage calculation tools.
4. Importance of Accurate Dosage Calculation
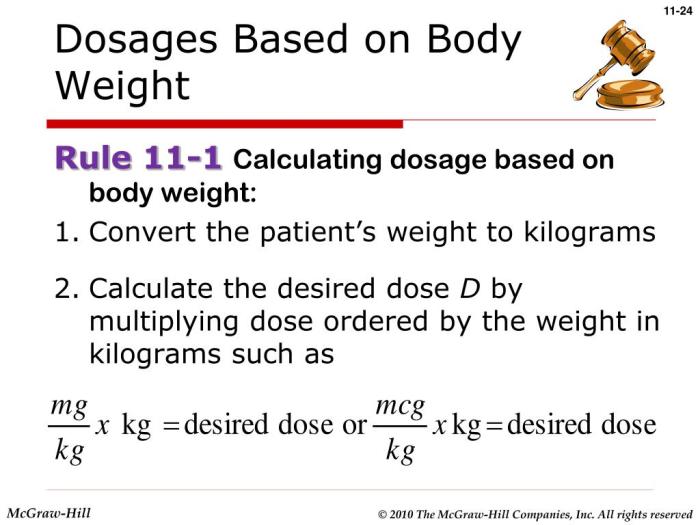
Accurate dosage calculation is crucial in healthcare as it ensures that patients receive the correct dosage for their specific needs.
Risks of Incorrect Dosage Calculations
Incorrect dosage calculations can lead to:
- Adverse drug reactions
- Medication errors
- Patient harm
Patient Safety and Well-being
Accurate dosage calculation contributes to patient safety and well-being by ensuring that patients receive the appropriate treatment for their condition.
5. Dosage Calculation in Practice
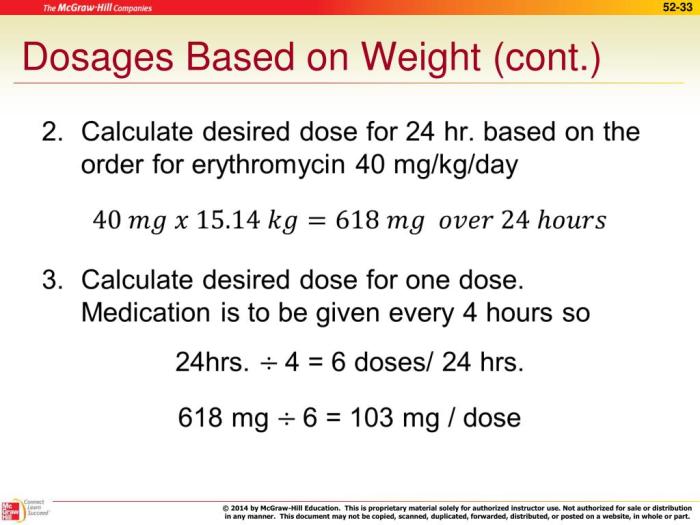
Dosage calculation by weight is widely used in clinical settings:
Responsibilities of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, such as nurses and pharmacists, are responsible for ensuring accurate dosage calculations.
Best Practices, Dosage calculation 3.0 dosage by weight test
Best practices for dosage calculation include:
- Using standardized formulas and guidelines.
- Verifying dosage calculations with a second healthcare professional.
- Documenting dosage calculations accurately.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key advantages of using Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test?
Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test offers several key advantages, including improved accuracy, reduced risk of errors, enhanced efficiency, and streamlined documentation.
How does Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test ensure accurate dosing?
Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test utilizes advanced algorithms and built-in safety checks to minimize the risk of errors and ensure precise dosage calculations.
What types of medications can be calculated using Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test?
Dosage Calculation 3.0 Dosage by Weight Test supports a wide range of medications, including oral, intravenous, and intramuscular formulations.