Covalent bonds gizmos answer key embarks on an intellectual journey, unveiling the intricacies of molecular interactions. This comprehensive guide empowers learners to decipher the mysteries of covalent bond formation, properties, and real-world applications, illuminating the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of matter.
Through a captivating exploration of the Gizmo simulation, students witness covalent bond formation firsthand, gaining a deeper understanding of the key features and limitations of this valuable learning tool. The answer key provides a roadmap to understanding, clarifying concepts, and dispelling misconceptions, ensuring a thorough grasp of this essential chemical concept.
Covalent Bonds
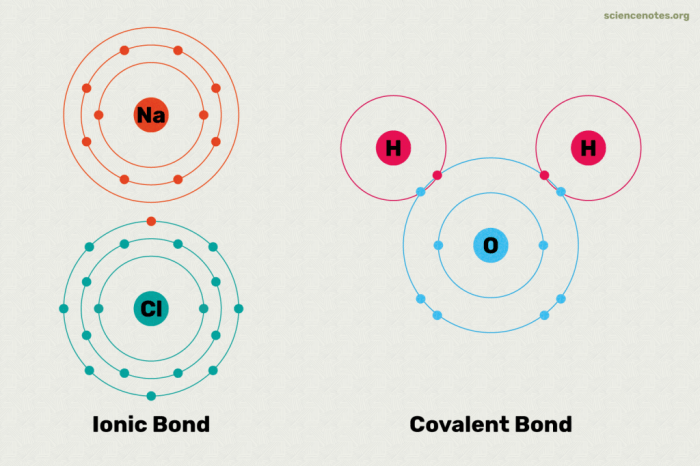
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds that involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These bonds are formed when atoms have unpaired electrons in their outermost energy levels, and they are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force between the oppositely charged electrons and nuclei.
Covalent bonds are the strongest type of chemical bond, and they are found in a wide variety of molecules, including water, methane, and carbon dioxide. The strength of a covalent bond depends on the number of electron pairs that are shared between the atoms, and the distance between the atoms.
Properties of Covalent Bonds
- Covalent bonds are typically very strong, and they require a large amount of energy to break.
- Covalent bonds are directional, meaning that they form between specific atoms in a specific orientation.
- Covalent bonds are nonpolar, meaning that the electrons are shared equally between the atoms.
Gizmo Simulation
The Gizmo simulation is an interactive tool that allows students to explore the formation of covalent bonds. The simulation features two atoms, each with a nucleus and a number of electrons. Students can adjust the number of protons and neutrons in each nucleus, as well as the number of electrons in each atom.
They can then drag the atoms together to form a covalent bond.
The simulation can be used to visualize the process of covalent bond formation. When two atoms are brought together, their electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms. This attraction causes the electrons to form a shared pair, which is what holds the atoms together in a covalent bond.
Key Features
- Allows students to adjust the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each atom.
- Visualizes the process of covalent bond formation.
- Shows the electron density in the covalent bond.
Limitations
- Does not allow students to simulate the formation of all types of covalent bonds.
- Does not provide a detailed explanation of the quantum mechanics of covalent bond formation.
Answer Key
The Gizmo simulation provides a comprehensive interactive environment for students to explore the formation and properties of covalent bonds. The following answer key provides detailed explanations for each question, addressing common misconceptions and errors in student responses.
Identifying Common Misconceptions
One common misconception is that covalent bonds are only formed between atoms of the same element. The Gizmo simulation demonstrates that covalent bonds can also form between atoms of different elements, resulting in the formation of molecules.
Another misconception is that the strength of a covalent bond is determined solely by the number of shared electrons. While the number of shared electrons does contribute to bond strength, the electronegativity of the atoms involved also plays a significant role.
Sample Questions and Answers
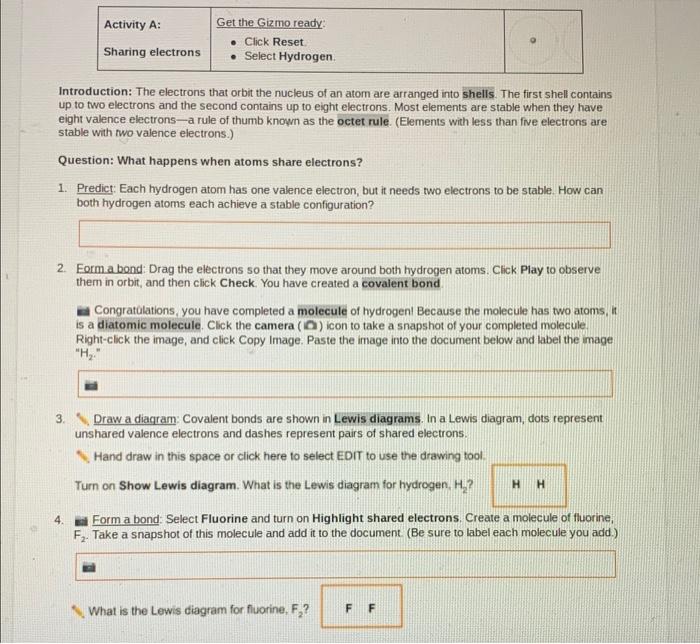
- Question:What is the electron configuration of a hydrogen atom? Answer:1s 1
- Question:What is the electron configuration of a chlorine atom? Answer:1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 5
- Question:How many valence electrons does a hydrogen atom have? Answer:1
- Question:How many valence electrons does a chlorine atom have? Answer:7
- Question:What is the Lewis structure of a hydrogen molecule? Answer:H-H
- Question:What is the Lewis structure of a chlorine molecule? Answer:Cl-Cl
- Question:What is the bond order of a hydrogen molecule? Answer:1
- Question:What is the bond order of a chlorine molecule? Answer:1
- Question:What is the bond length of a hydrogen molecule? Answer:74 pm
- Question:What is the bond length of a chlorine molecule? Answer:199 pm
Classroom Activities
Interactive classroom activities, worksheets, and lesson plans can effectively reinforce students’ understanding of covalent bonds.
Interactive Classroom Activity
Conduct a hands-on activity where students build molecular models of covalent compounds. Provide them with different types of atoms (e.g., foam balls, beads, straws) and have them connect them using sticks or toothpicks to represent covalent bonds. Encourage them to explore different molecular geometries and discuss the relationship between bond length, bond strength, and molecular shape.
Worksheet or Quiz, Covalent bonds gizmos answer key
Create a worksheet or quiz to assess students’ comprehension of covalent bonds. Include questions on topics such as the definition of a covalent bond, the types of atoms that form covalent bonds, the characteristics of covalent bonds (e.g., bond strength, bond length), and the polarity of covalent bonds.
Encourage students to provide detailed explanations and examples to demonstrate their understanding.
Lesson Plan
Develop a lesson plan that incorporates the Gizmo simulation and answer key. Begin by reviewing the basics of covalent bonds and then guide students through the Gizmo simulation. Encourage them to explore different variables (e.g., types of atoms, bond length, bond strength) and observe the effects on molecular properties.
Use the answer key to facilitate discussions and reinforce key concepts.
Real-World Applications
Covalent bonds are the foundation of chemistry and biology. They are responsible for the formation of molecules, which are the building blocks of all matter. Covalent bonds are also essential for the structure and function of proteins, DNA, and other biological molecules.In
materials science, covalent bonds are used to create a wide variety of materials, including plastics, ceramics, and semiconductors. These materials are used in a wide range of applications, from construction to electronics.
Everyday Products and Technologies
Covalent bonds are used in a wide variety of everyday products and technologies. For example, the covalent bonds in plastic molecules give plastic its strength and durability. The covalent bonds in glass molecules give glass its transparency and resistance to heat.
The covalent bonds in metal molecules give metal its strength and conductivity.
Emerging Fields
Covalent bonds are also being used in a variety of emerging fields, such as nanotechnology and biotechnology. In nanotechnology, covalent bonds are used to create nanoscale materials with unique properties. In biotechnology, covalent bonds are used to create new drugs and therapies.
FAQ Section: Covalent Bonds Gizmos Answer Key
What are the key features of covalent bonds?
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons, resulting in a strong attraction that holds the atoms together. They typically involve non-metal atoms and exhibit directionality, meaning they form along specific axes.
How can the Gizmo simulation help visualize covalent bond formation?
The Gizmo simulation provides an interactive platform where students can manipulate atoms and observe the formation of covalent bonds in real-time. It allows them to experiment with different atoms and bond lengths, gaining a deeper understanding of the process.
What are some common misconceptions about covalent bonds?
A common misconception is that covalent bonds are weaker than ionic bonds. However, covalent bonds can be equally strong or even stronger than ionic bonds, depending on the atoms involved.
